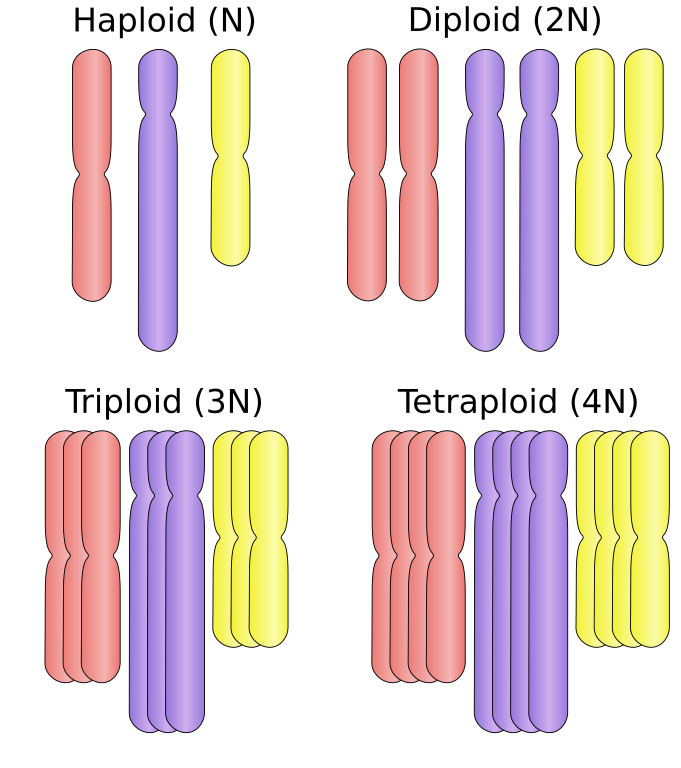
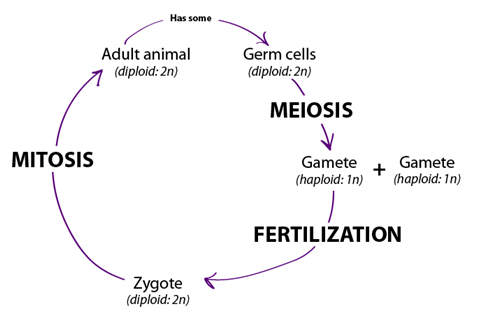
Gametes are haploid cells produced by the process of meiosis. They unite during fertilization to form a diploid zygote, which divides to form the embryo, and is the first cell of the new offspring of the organisms that produced the gametes. Haploid cells are a result of the process of meiosis, a type of reductional cell division in which diploid cells divide to give rise to haploid germ cells or spores. During meiosis, a diploid germ cell divides to give rise to four haploid cells in two rounds of cell division. Start studying Chapter 5: Cell growth and division. Learn vocabulary. Gametes 23 chromosomes 1 set. Are the cells at the end of mitosis haploid or diploid?
Editplus 2.11. A gamete is a specialized germ cell that fuses with another gamete during fertilization (conception) in organisms that reproduce sexually. In species which produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual which produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum (or egg)—and a male produces the smaller type—called a spermatozoon (or sperm cell) in animals, and a pollen grain in higher plants. The creation of gametes is gametogenesis, and during it gametocytes divide by meiosis into gametes. Organs that produce gametes are called gonads in animals, and archegonia or antheridia in plants.
The term gamete comes from the ancient Greek γαμετης (spouse). Gametes are haploid cells; that is, they contain one complete set of chromosomes (the actual number varies from species to species). When two gametes fuse (in animals typically involving a sperm and an egg), they form a zygote—a cell that has two complete sets of chromosomes and therefore is diploid. The zygote receives one set of chromosomes from each of the two gametes through the fusion of the two gamete nuclei.
After multiple cell divisions and cellular differentiation, a zygote develops, first into an embryo, and ultimately into a mature individual capable of producing gametes. Gametes from a mature diploid individual are produced in the gonadal tissue through meiosis —a process of cellular division that reduces the number of sets of chromosomes from two to one (i.e., produces haploid gametes). The diploid somatic cells of an individual contains one copy of the chromosome set from the sperm and one copy of the chromosome set from the egg; that is, the cells of the offspring have genes expressing characteristics of both the father and the mother.